
Cattle Farming
Cattle farming involves the rearing and management of two types of animals- one group for food requirements like milk and another for labour purposes like ploughing, irrigation, etc. Animals which provide milk are called milk/dairy animals. For example, goats, buffalo, cows, etc. Animals which are used for labour are called draught animals.
Since dairy animals are cared for and bred for milk, we need to improve milk production to meet the requirements. The period after the birth of a calf, when a cow starts to produce milk, is called the lactation period. We can enhance milk production by increasing this lactation period. But along with milk production, quality must also meet. Dairy farm management is the management of the milk animals with the goal of enhancing the quantity and quality of the milk produced. For this reason, high-yielding and disease-resistant breeds are developed.
Farm Management
Cattle farming is not all about milk or meat production. It also comes with some responsibilities. To meet human requirements, we need to take good care and need proper management of livestock.
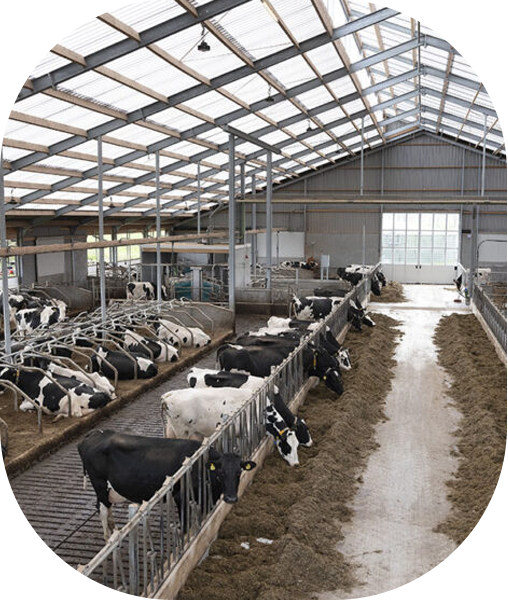
Shelter
In cattle farming, animals are maintained in a strictly hygienic manner with proper housing. For maintenance, we need to follow some routines.
- Animals and their sheds need to be cleaned at regular intervals.
- Animals should be brushed regularly to remove the dirt and bugs in their body.
- The shed should be well-ventilated and roofed so that animals are protected from rain, heat, and cold.
- A proper drainage system should be there to remove animal waste.
Food
Food requirements of animals are also a part of cattle farming. To maintain high-yielding and disease-resistant breeds, they must be provided with an adequate water supply and nutrient-rich fodder regularly according to their needs. In cattle farming, two factors are considered regarding the food of cattle. The food that is provided must keep the animals healthy as well as should meet the farming requirement. Hence, animal feed includes roughage (high fibre content) and concentrates (high proteins and nutrient content). In addition to this, supplements containing micronutrients are also provided to animals. An adequate proportion of these rations promote healthy and high-output animals.


Disease Management
The third responsibility of cattle farming management is to maintain disease-free breeds. Animals are not an exception to disease. They also suffer from numerous diseases. This may affect the health as well as productivity of animals; even cause their death. Parasites, bacteria, and viruses are the major villains here. These microbes infect the cattle externally as well as internally. Vaccination is the one solution for the protection against bacterial and viral infections.
